Top 10 IT Software companies in Vizag
Posted on January 02, 2026

Caching makes your WordPress site load quickly and responsive, although in certain circumstances, the cache files can interfere with updating the site, making them change stylings or trying to troubleshoot. Around 16.2% of all websites use some form of caching technology.
If you are wondering How to Clear Cache in WordPress; this step by step guide will walk you through five simple methods to remove old cached files.
Cache Flushed versions of your web pages, images, scripts and database queries that are stored temporarily. Rather than your server taking time to create a page every time a person visits, WordPress loads the page using the cached copies; thus, it takes a shorter time to create the page. This will ease the load on the servers and enhance the user experience.
The use of caching is usually achieved in various levels:
All these caching tiers come to play in ensuring that your site loads fast and uses fewer resources.
While cache improves performance, it can sometimes cause problems. Clearing it becomes necessary when the cached version does not match the latest updates made to your website.

This is the reason why it is important to clear WordPress cache:
Modified text, images, styling and code can continue to appear on the old content on the cache pages. The clearing of the cache will ensure that WordPress and the browser load the latest version.
CSS and JavaScript are prone to becoming stuck behind cache files. Clearing the cache is a sure way of loading your new files properly.
The cache can cause conflicts with new scripts when installation is made of a new plugin or when a major change is made to your theme. Deleting it will make sure that there will be no remnants of files.
Cached files can also cause page layout or functionality incompatibilities in case you change hosting, move your site, or change database settings.
Developers have to see real time changes. The bugs can be covered with cache or indicate old code.
When you have clouds, sucuri, or performance caches, such as LiteSpeed, then you can end up in loops or sending out-of-date responses as a result of mismatched caches.
A cache may reside in many formats: in your browser, in WordPress caching plugins, in server-level cache or it can be a CDN. The option of clearing all the relevant caches will make the visitors view the latest version of your pages. Five practical steps, which include those areas, are listed below.
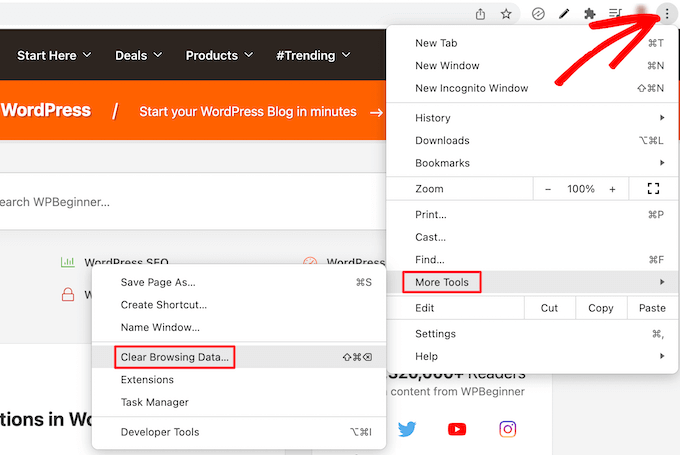
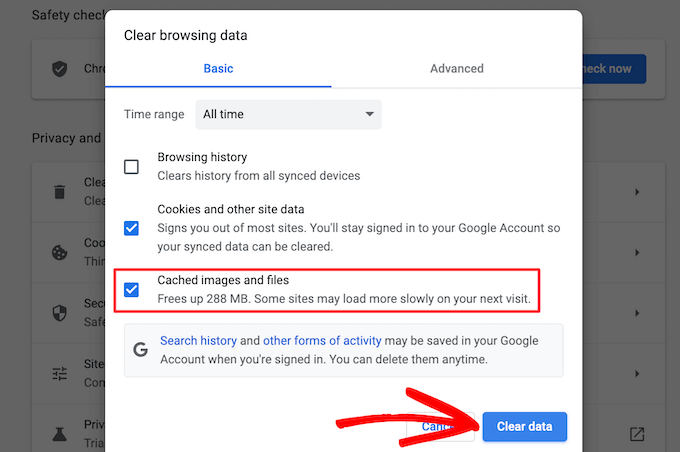
If you have modified a page and are not seeing the modification, the first simple task would be to clear the browser cache. All browsers have local copies of pages and other resources such as images and scripts. Deleting it causes the browser to reload new files on your server.
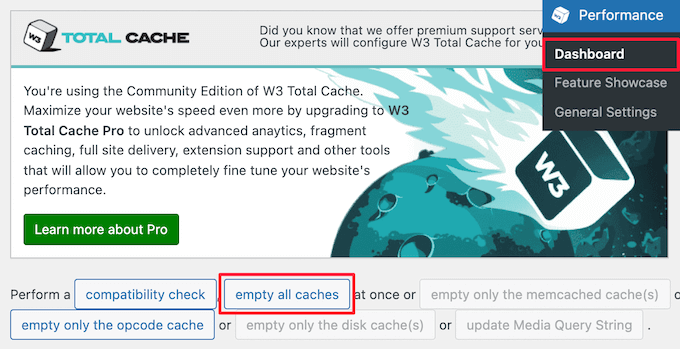
With a caching plugin, they tend to save caching HTML and assets in order to deliver faster. The most popular ones are WP Super cache, W3 total cache, WP Fastest cache and LiteSpeed Cache. Go to the settings of your WordPress administration, find the clear/purge/ delete button in the plugins section and click it. It is also possible to have one click purging through most of the available plugins with an admin toolbar button.
This action solves the majority of display problems because the biggest source of stale content is usually the cache of the plug-ins.
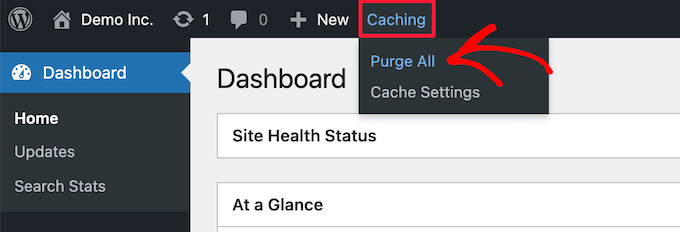
Most WordPress managed hosts deploy server side caching in an effort to enhance performance. This layer intervenes between your site and the visitors and it can preserve the old content unless it is cleared out of your hosting account.
Find an option in your host control panel which says Cache, Caching or Server Cache and empty or clear out the cache. It is always safe to ask your host support to clear the server cache of your site in case of doubt.
Content delivery networks store files at edge locations around the world. This is because when you rewrite a page or asset the CDN can continue serving the old version until you invalidate or purge it.
Open the dashboard of your CDN and pick the site or asset and either pick Purge or Invalidate. Certain CDNs also permit purges to be done based on URL, useful when only one resource is required to be refreshed.
If you do not use a CDN, skip this step.
Old data may also be stored in advanced caching systems like object cache (transient object caching and database object caching) and opcode cache (PHP bytecode). Examples of object cache solutions are Redis and Memcached. Philippine PHP extensions like OPcache tend to support opcode caching.
Removing these caches would usually demand a control panel of a server, a hosting control or a command line. When you are not able to control the server, instruct your host to empty objects and opcode caches.
Most users only require this step when code changes or updates to the plugins are not reflected on performing other caches clearing.
If you ever need to know how to remove cache from wordpress completely, follow the five steps above and confirm that each cache layer is purged. The whole path of the browser CDN server is under one term.
You should clear cache whenever you:
The maintenance of clearing cache is a mandatory procedure that makes your site display up to date material and behave as expected. Follow these five steps and you will easily master How to Clear Cache in WordPress, whether the issue lives in your browser, a plugin, your hosting layer, or a CDN. Consistent caching process enables you to provide a high speed and accuracy at the same time.
Clear cache after updating some significant changes, altering styles or in case of troubleshooting. Often routine changes are done by regular automatic purge settings.
Users can see a milder version of the same issue when they immediately clear their browsers which results in slower loading initially whilst caches are rebuilt, but after that they are back to their usual speed.
Purge activities are not very dangerous. When you are using object or opcode cache, it is good to make a backup first or seek the help of the host support.
Look or errors in check of conflicting plug in, theme problems or hard coded files. Check DNS propagation also in case of change in domains or hosts.