Top 10 IT Software companies in Vizag
Posted on January 02, 2026
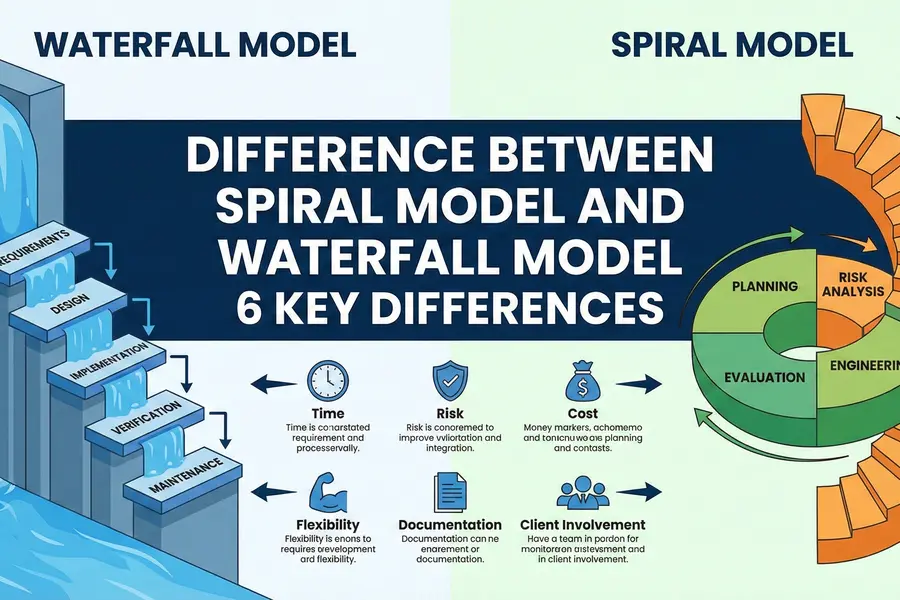
When choosing a development approach, understanding the difference between spiral model and waterfall model helps teams match risk, complexity, and customer needs to the right process. These two models have been used to inform software engineering practices over decades, but they are very appropriate in different types of projects.
In this article, we have identified six distinct differences, different criteria of selecting each model, and practical tips so that you could confidently choose what to select.
The waterfall model is a sequential linear operation of processes like requirements, design, implementation, testing and maintenance. The phases are completed successively, so the planning is easy but there is no space to make changes.
The spiral model involves the use of iterative development and systematic risk analysis. Projects are achieved by cyclic processes which consist of planning, risk analysis and assessment, engineering and evaluation. This method is most appropriate in a complicated or risky project where the requirements can change.
2024 analysis consolidating over 1,250 IT projects found that agile/iterative methods increased project success rates by about 21% compared to traditional plan-driven methods.
There are six main differences that are critical when the real project is being managed.
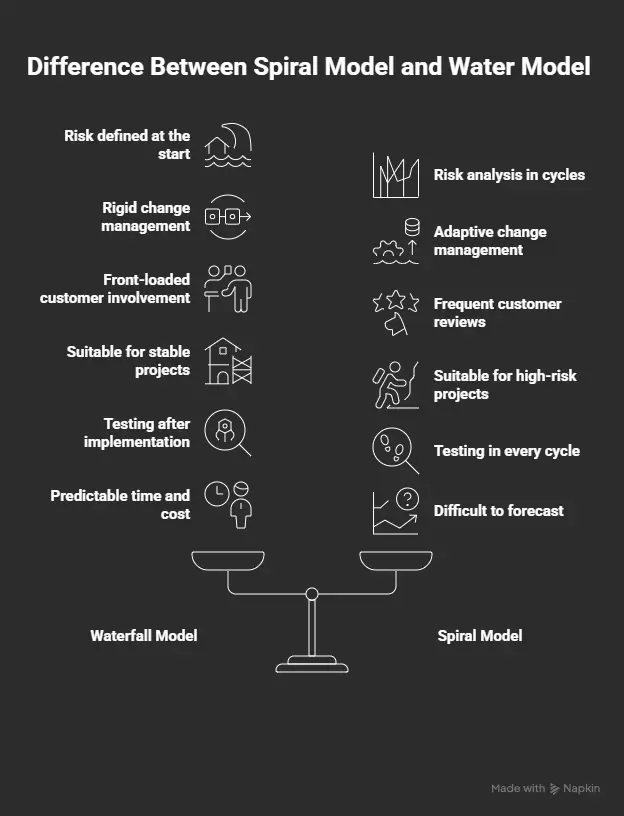
Waterfall defines risk as a definite issue addressed at the beginning of requirements and design. After such phases are taken care the model presumes that the risks are low or controllable.
Spiral uses risk analysis as the centre of focus of every cycle. The teams detect, prioritize and mitigate risks during the project. This renders the spiral model much more robust in a project where there are unknowns in the project.
The waterfall is rigid. Post requirements modifications are challenging and expensive as downstream operations presuppose constant inputs.
Spiral is adaptive. The iterations give the chance to update requirements and design in accordance with the feedback and new data. The cost of late changes is minimized by this flexibility in the evolving projects.
Waterfall model customer engagement is front loaded. At the beginning, requirements are defined by stakeholders and at the end deliverables are usually reviewed.
Spiral model promotes frequent reviews of customers after every iteration. This feedback loop is common and it facilitates in ensuring the product keeps on track with the needs of the users as different needs are experienced with time.
Waterfall is appropriate in projects where the requirements are stable, well known like the internal tools whose requirements have clear regulatory boundaries or simple web sites.
Spiral will best suit high risk, research oriented or large scope systems whose requirements are uncertain or where technologies are new. Spiiral is a good option, in case of interest in risk minimization and regular verification.
A unique phase implemented after implementation is in waterfall testing. Although this makes scheduling easier, it may permit the piling of defects to occur towards the end of the project life cycle.
Spiral incorporates testing every single cycle. Initial prototyping and continued testing and assessment brings out defects earlier in the process and corrections can be made gradually, thus improving overall quality and minimizing late rework.
Waterfall offers predictable deadlines and budgets in case the requirements are fixed. It is more linear and thus makes delivery estimation and resource allocation more comfortable.
Spiral has a greater difficulty to forecast since every cycle might have new discoveries that would cost extra time or money. Nevertheless, spiral minimizes the probability of disastrous overruns since risks are exposed at an early stage and choices provided on how to reduce them.
In the practical sense, the difference between waterfall model and spiral model in software engineering is reduced to predictability and adaptability. Waterfall provides predictiveness that is organized and is effective when the inputs are known. Spiral provides flexibility and risk management that is appropriate on projects where uncertainty is the key factor. Make a selection depending on whether the rigid milestones are required or the iterative validation.
Choose waterfall Model when:
Choose spiral Model when:
These two models are worthy and useful at work. The difference between spiral model and waterfall model is not about which is better in absolute terms but about which one fits the project context. Waterfall is bright in predictability and clarity whereas spiral is good in uncertainty and risk management. Assess your risks, need stability and your stakeholders need to choose the appropriate path.
Yes. It is typical to use hybrid approaches. Waterfall is used frequently in the established components that are of low risk, and spiral cycles are used in uncertain and high-risk components.
Small software teams and startups are more inclined to iterative methods that resemble spirals since they can learn quickly and correct the course through the development of product ideas.
Agile has features of spiral like frequent feedback and iterative delivery. Agile is more inclined to team practices and ceremonies whereas spiral is concerned with formal risk analysis at every cycle.
Not necessarily. Spiral might need additional planning and review steps to accomplish but can shorten complex projects to time-to-market due to the reduction of unwarranted costly rework and the spiral approach can solve this.