Top 10 IT Software companies in Vizag
Posted on January 02, 2026
![What is Programmatic SEO [2026 Edition]](https://www.helpingcontent.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/What-is-Programmatic-SEO-in-2026.png)
Just imagine how easy your life is going to be when you are creating hundreds and thousands of webpages without writing line-by-line. Sounds magical? That is what programmatic SEO has to offer to you. But, what is programmatic SEO? Well, it is a new SEO method which allows websites to create pages in bulk by using templates and stored data.
Large platforms such as TripAdvisor, Zillow, and Nomad List already rely on this setup to appear for massive keyword ranges. Instead of producing content page by page, a structured system creates pages automatically using existing data. This method reduces effort and helps websites reach users searching for very specific terms.
It is worthwhile to know what SEO is before we know more about programmatic SEO. SEO involves optimizing a site so that it is more visible in the search engines, such as Google. When people search online, Google displays many results. SEO helps a site appear closer to the top. Higher placement leads to more visits. That is the core idea.
Programmatic SEO is more like a production line, except that instead of physical products, it generates web pages. One main template is created and different data fills it to form separate pages.
Each page focuses on a unique keyword pattern.
For an example, a travel website can create pages such as:
Instead of writing every page manually, the template pulls city names from a database. The system handles the rest.
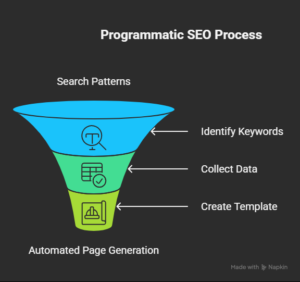
Step 1: Identify Search Patterns
Find keywords in which the search intent remains unchanged, but the words are changed minorly. Examples would be things like coffee shops in [city name] or best [product type] under [price].
Step 2: Collect Your Data
Keep all the necessary data in a systematic format. A spreadsheet, table, or database works well.
Step 3: Create a Template
Design a one-page layout with empty fields where data will appear. This layout becomes the base for every page.
Step 4: Automate the Generation
Use tools or scripts to merge data with the template. Each data set creates a new page.
| Component | What It Is | Example |
| Data Source | Organized information | Spreadsheet with cities, prices, features |
| Template | Page layout with placeholders | HTML page with [CITY], [PRICE] |
| Generation System | Tool that connects data to template | WordPress plugin, Python script, no-code tool |
| Hosting | Platform where pages exist | WordPress, Webflow, custom site |
All components must work together for programmatic SEO to succeed.
Scale stands out as the main benefit, but several other advantages matter just as much.
Time Savings:
Cost Efficiency:
Consistency:
Scalability:
These programmatic SEO examples show how major platforms use this strategy to capture search traffic.
1. TripAdvisor
Builds millions of pages for hotels, dining spots, and attractions. Reviews, ratings, photos, and location details come directly from stored data.
2. Zillow
Creates pages for every property search combination. Searches like “homes for sale in [city]” or “[property type] in [area]” all lead to structured pages.
3. Nomad List
Publishes city pages for remote workers with data on living costs, internet quality, safety, and climate. One format powers all pages.
4. Amazon
Uses the identical product page design with varied product information, reviews, and recommendations on millions of products listings.
Effective programmatic pages are balanced between structure and utility. Here are the best practices to follow for success in programmatic SEO in 2026:
Focus on User Value:
Ensure Content Uniqueness:
Optimize Technical SEO:
Build Smart Internal Links:
Programmatic SEO is not applicable to every type of web site.
It Works Well For:
It Doesn’t Work For:
Suggested Reading: Advantages and Disadvantages of SEO
Regular SEO is when the pages are created sequentially. Programmatic SEO automates the creation of pages based on data and templates. It works like mass production instead of manual work.
Yes, poor execution leads to issues. Thin or duplicate pages cause ranking problems. Useful and well-structured content avoids penalties.
There is no fixed number. Pages should only exist when data adds real value. A smaller set of strong pages always performs better.